Table of contents
No headings in the article.
This a tut for beginners to be introduced to git and github and can resolve each conflicts by this .
It’s easy to apply these concepts and if you get stuck take that as a hurdle and cross it over 🤗
GIT : An open source version control system for controlling or managing a project through the history and mentions too.
GITHUB : A platform where git implements
Database or a server is like git and the website of that is like github
Some commands for GIT:
mkdir project : makes directory
ls : for showing the list of the files avalaible in that repository
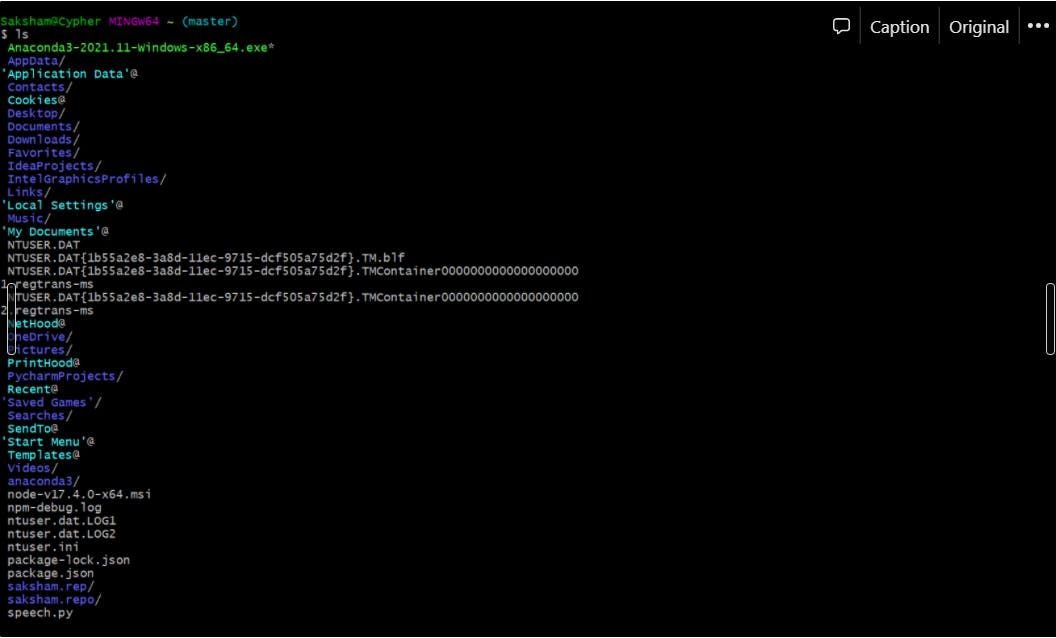
cd : change directory
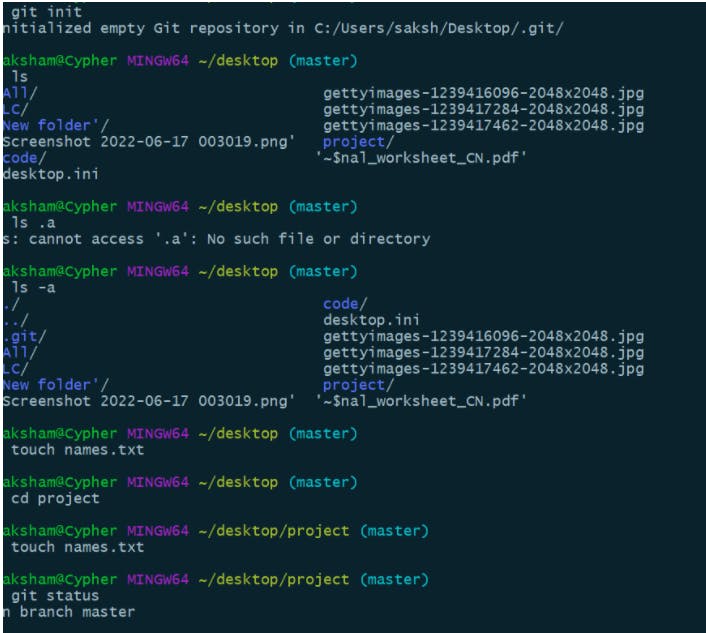
touch names.txt : creates a file
git init : to create that git environment or adding it to the repository
ls -a : shows the hidden file such as .git .. and so one
git status : displays the status of the commits
git add . : adds all the untracked files
git add project_name : add only project_name to the git or history
git commit -m “adding a message” : adding a message to a commit
vi file_name : to edit the file inside the bash only ( also called as vim)
cat names.txt : displays the content inside the text file
git restore —staged names.txt : remove without commiting
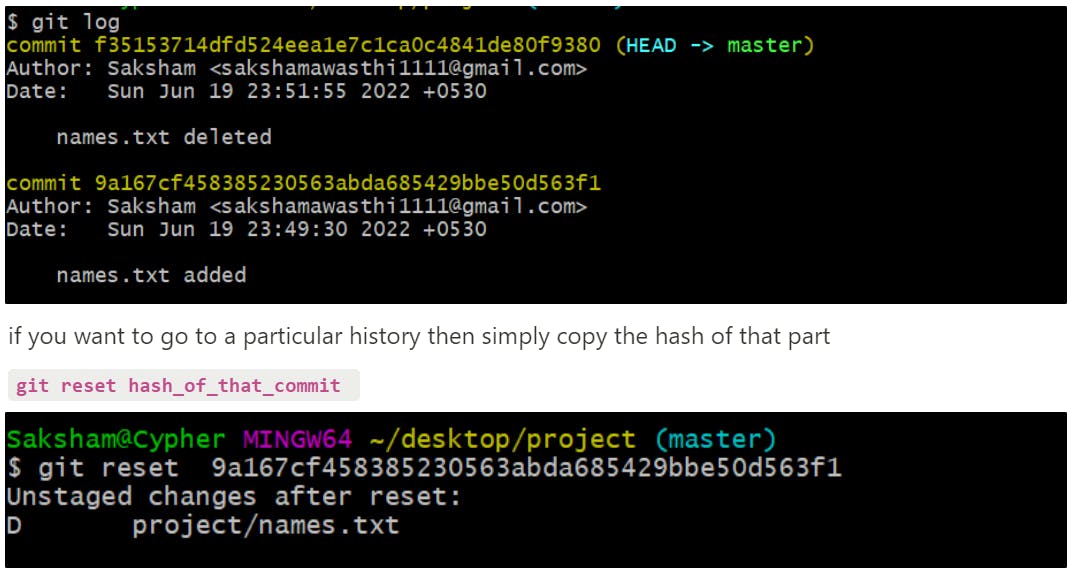
git log : to see the history of all commits
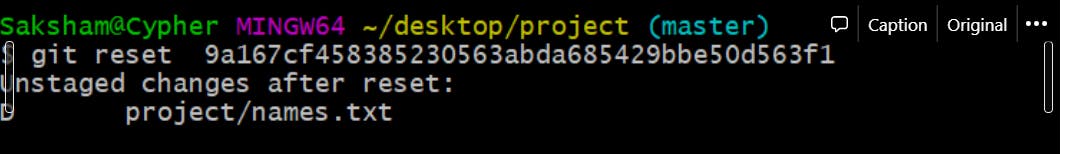
Each commit has a hash id which leads us to the point that we cant just delete a commit but can unstage it
Stashing the files : Its like putting those files backstage and if they are required can be pulled back
firstly add all the commits
git stash
all the data that was updated was sended to the stash
git stash pop : bring from backstage to the mainline
git stash clear : clears the backstage clearly
Connecting Remote repositories to local repo
git remote add origin link_for_the_remote_repo :
Remote : working with urls
add : adding somethin
origin : name of the url link
basically all the repos which are of your own have origin tag on them
git remote -v : tells the URL’s attatched to the folder
To push the commits to the remote repo
GIT PUSH
format : git push URL branch : SO in our case it’s git push origin master
What is Branch
a unique set of code changes with a unique name . Each repository can have one or more branches. The main branch — the one where all changes eventually get merged back into, and is called master.
For cloning a project :
Firstly to fork it as you cant directly make changes to anyones code
git clone URL
Checkout : Head will come to that branch git checkout
What is a pull request ?
We have created a fork version of the code which we are changing of ny other’s code but when we are done with it we can ask the original user to change the code to our forked one .
So for this asking from the user is called pull request
Why to maintain multiple branches or main branch?
We want to open new pull request for each bug or task and 1 branch can do 1 PR only ….
If we make a single branch instead of main only then it also have multiple commits like it would be impossible to review the code for each bug or cant discuss it
when the commits in local are extra than remote one than you have to force push it as all are interlinked and have to make their existance is a better way
Once the commits are deleted they would be deleted from the branch but would be there in the upstream
So for deleting that we need to fetch all the files which are present and the deleted one as well
How to merge all the commits into a single commit ?
By rebase command
git rebase -i hash : i is here for intersections
then push and squash the commits to be pushed comes under that and the one to be merged in all is to be done using s that is squashed
RESET :
for resetting the commit with permanent we use git reset — hard 9a403b6a97ec00101908cf174ad0b2f5fce3ae96
Merge Conflicts :
you changed on line number 3 and someone else made it too…
then git will ask you that which change to be taken
change the conflicts which are overriding and you are good to go
That’s it with the git and github tutorial … Hope you find it useful …
💖Enjoy ur day/night
